Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: isometheptene mucate, dichloralphenazone, and acetaminophen
Dosage form: capsule
Drug class: Antimigraine agents
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Mar 25, 2025.
On This Page
CAUTION
This product contains acetaminophen. Severe liver damage may occur if a person takes:
- More than 4,000 mg of acetaminophen in 24 hours
- With other drugs containing acetaminophen
- With 3 or more alcoholic drinks everyday while using this product.
Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules Description
Each Isometheptene Mucate, Dichloralphenazone, and Acetaminophen Capsule contains:
| Isometheptene Mucate | 65 mg |
| Dichloralphenazone | 100 mg |
| Acetaminophen | 325 mg |
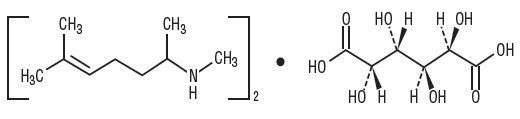
Isometheptene Mucate is a white crystalline powder having a characteristic aromatic odor and bitter taste. It is an unsaturated aliphatic amine with sympathomimetic properties. Its molecular weight is 492.65 and it has the following structural formula:
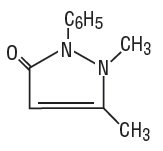
Dichloralphenazone is a white, microcrystalline powder, with slight odor and tastes saline at first, becoming acrid. It is a mild sedative. Its molecular weight is 519.07 and it has the following structural formula:
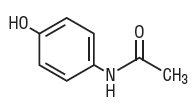
Acetaminophen, a non-salicylate, occurs as a white, odorless, crystalline powder, possessing a slightly bitter taste. Its molecular weight is 151.16 and it has the following structural formula:
The inactive ingredients are: gelatin, lactose anhydrous, silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C yellow 5, carmine and titanium dioxide.
Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules - Clinical Pharmacology
Isometheptene Mucate, a sympathomimetic amine, acts by constricting dilated cranial and cerebral arterioles, thus reducing the stimuli that lead to vascular headaches.
Dichloralphenazone, a mild sedative, reduces the patient's emotional reaction to the pain of both vascular and tension headaches.
Acetaminophen raises the threshold to painful stimuli, thus exerting an analgesic effect against all types of headaches.
Indications and Usage for Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules
For relief of tension and vascular headaches.1
- 1
- Based on a review of this drug (isometheptene mucate) by the National Academy of Sciences-National Research Council and/or other information, FDA has classified the other indication as "possibly" effective in the treatment of migraine headache. Final classification of the less-than-effective indication requires further investigation.
Contraindications
Isometheptene Mucate, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen is contraindicated in:
- Hypersensitivity or intolerance to any component of this product
- Cardiovascular or cerebrovascular insufficiency, including recent myocardial infarction or stroke
- Glaucoma
- Severe cases of renal disease
- Hypertension
- Organic heart disease
- Peripheral vascular disease
- Hepatic disease
- Those patients who are on monoamine-oxidase (mao) inhibitor therapy
Warnings
Hepatotoxicity
Acetaminophen has been associated with cases of acute liver failure, at times resulting in liver transplant and death. Most of the cases of liver injury are associated with the use of acetaminophen at doses that exceed 4,000 milligrams per day, and often involve more than one acetaminophen-containing product. The excessive intake of acetaminophen may be intentional to cause self-harm or unintentional as patients attempt to obtain more pain relief or unknowingly take other acetaminophen-containing products. The risk of acute liver failure is higher in individuals with underlying liver disease and in individuals who ingest alcohol while taking acetaminophen.
Instruct patients to look for acetaminophen or APAP on package labels and not to use more than one product that contains acetaminophen. Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately upon ingestion of more than 4,000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day, even if they feel well.
Serious Skin Reactions
Rarely, acetaminophen may cause serious skin reactions such as acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) which can be fatal. Patients should be informed about the signs of severe skin reactions, and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Hypersensitivity/Anaphylaxis
There have been post-marketing reports of hypersensitivity and anaphylaxis associated with the use of acetaminophen. Clinical signs included swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, respiratory distress, urticaria, rash, pruritus, and vomiting. There were infrequent reports of life-threatening anaphylaxis requiring emergency medical attention. Instruct patients to discontinue Isometheptene Mucate, Dichloralphenazone, and Acetaminophen Capsules immediately and seek medical care if they experience these symptoms. Do not prescribe Isometheptene Mucate, Dichloralphenazone, and Acetaminophen Capsules for patients with acetaminophen allergy.
Precautions
Caution should be observed in hypertension, peripheral vascular disease and after recent cardiovascular attacks. This drug may make you dizzy or drowsy. Do not drive, use machinery, or do any activity that requires alertness until you are sure you can perform such activities safely. Avoid alcoholic beverages. Remember that alcohol may be a cause of headaches.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Do not take this product if you are allergic to any of its ingredients. If you develop signs of allergy such as rash or difficulty breathing stop taking this product and contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Do not take more than 4,000 milligrams of acetaminophen per day. Call your doctor if you took more than the recommended dose.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
This drug should not be used with the following medications because very serious interactions may occur:
- Sodium oxybate.
- Avoid MAO inhibitors (isocarboxazid, linezolid, methylene blue, moclobemide, phenelzine, procarbazine, rasagiline, selegiline, or tranylcypromine) within 2 weeks before, during, and after treatment with this medication. In some cases a serious (possibly fatal) drug interaction may occur.
- Consider drugs that cause drowsiness such as: certain antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine), anti-seizure drugs (e.g., carbamazepine, phenytoin), medicine for sleep or anxiety (e.g., alprazolam, diazepam, zolpidem), muscle relaxants (e.g., cyclobenzaprine), narcotic pain relievers (e.g., codeine), psychiatric medicines (e.g., chlorpromazine, risperidone, trazodone).
- This medication may interfere with certain laboratory tests (including certain urine glucose tests, urine catecholamine levels, urine 5-HIAA levels), possibly causing false test results.
PREGNANCY
FDA has not assigned a pregnancy category for acetaminophen, dichloralphenazone, or isometheptene. Acetaminophen is routinely used for short-term pain relief and fever in all stages of pregnancy.
Acetaminophen crosses the placenta and is believed to be safe in pregnancy when used intermittently for short durations. No controlled studies have been done to establish the safety of dichloralphenazone or isometheptene or of their combination with acetaminophen. Isometheptene Mucate, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules, USP should only be given during pregnancy when need has been clearly established.
NURSING MOTHERS
Acetaminophen is excreted into human milk in small concentrations. Metabolites of dichloralphenazone are excreted into human milk. There are no data on the excretion of isometheptene into human milk.
Problems in humans have not been documented.
PEDIATRIC USE
Studies with this medicine have been done only in adult patients, and there is no specific information about its use in children.
GERIATRIC
There is no specific published information comparing use of this combination medicine in the elderly with use in other age groups. Geriatric patients are more likely to have peripheral vascular disease, and are therefore more likely to be adversely affected by peripheral vasoconstriction, than are younger adults. However, isometheptene may be safer for elderly patients than the ergot derivatives used to abort acute vascular headaches. Also, elderly patients are more likely to have age related renal function impairment, which may require caution in patients receiving acetaminophen and isometheptene.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
There is a potential for allergic reactions (e.g., swelling of the face, mouth, and throat, difficulty breathing, itching, or rash). A very serious allergic reaction, called anaphylaxis, to this drug is unlikely, but if it occurs, discontinue the drug and seek immediate medical attention.
Transient dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea may occur. This can usually be eliminated by reducing the dose. If any of these effects persist or worsen, notify your doctor or pharmacist promptly.
Call your doctor or physician for medical advice about side effects. To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Vilvet Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at (888)705-4369 or FDA at 800-FDA-1088, www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Overdosage
If overdose is suspected, contact your local poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. Symptoms of overdose may include: restlessness, severe drowsiness/dizziness, low body temperature, fast/slow breathing, fast/slow/irregular heartbeat, and unresponsiveness.
In acetaminophen overdosage: dose-dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis is the most serious adverse effect. Renal tubular necrosis, hypoglycemic coma and coagulation defects may also occur. Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxic overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis and general malaise. Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours post-ingestion.
Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules Dosage and Administration
Do not exceed the recommended dosage because severe liver damage may occur.
Tell your doctor about all usage of pain relievers.
For relief of migraine headache:
- The usual adult dosage is two capsules at once, followed by one capsule every hour until relieved, up to 5 capsules within a twelve-hour period.
For relief of tension headache:
- The usual adult dosage is one or two capsules every four hours up to 8 capsules a day.
How is Isometheptene, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen Capsules supplied
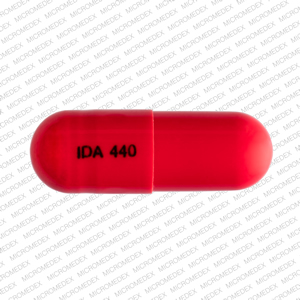
Isometheptene Mucate, Dichloralphenazone and Acetaminophen capsules are supplied as red capsules imprinted with VIP112 in bottles of 100ct, 71186-005-35.
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATION OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN. IN CASE OF ACCIDENTAL OVERDOSE, CALL A DOCTOR OR CONTACT A POISON CONTROL CENTER IMMEDIATELY.
| ISOMETHEPTENE MUCATE, DICHLORALPHENAZONE, AND ACETAMINOPHEN
isometheptene mucate, dichloralphenazone, and acetaminophen capsule, gelatin coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Vilvet Pharmaceuticals Inc (080444356) |
More about acetaminophen / dichloralphenazone / isometheptene mucate
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Reviews (108)
- Drug images
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Drug class: antimigraine agents